Protein kinase CK2 is an enzyme that regulates numerous cellular processes essential for development and differentiation. Its deregulation is observed in many diseases, including cancer, making this protein an attractive target for the development of pharmacological inhibitors.
Most inhibitors prevent ATP binding in the catalytic site of CK2. However, this type of inhibition suffers from a lack of specificity due to the high sequence homology of protein kinases at their catalytic site and the emergence of resistance phenomena. Targeting domains distant from the catalytic site represents a promising alternative for overcoming these limitations.
In this context, researchers from the Biosanté / Cellular mechanisms of invasion in angiogenesis and cancer team, in collaboration with chemists from the Faculty of Pharmacy in Lyon (INSERM 1052, CNRS 5286) have identified AB668, a bivalent chemical molecule that inhibits CK2 activity with a high degree of specificity by binding simultaneously to its catalytic site and to an adjacent hydrophobic pocket
aD (Figure).
Moreover, AB668 induces apoptotic death in numerous cell lines derived from aggressive cancers while sparing healthy cells.
These results suggest that AB668 represents a promising new anti-cancer pharmacological agent by attacking only tumour cells. For the researchers, the next step will be to test the molecule after optimization in pre-clinical models of various cancers.
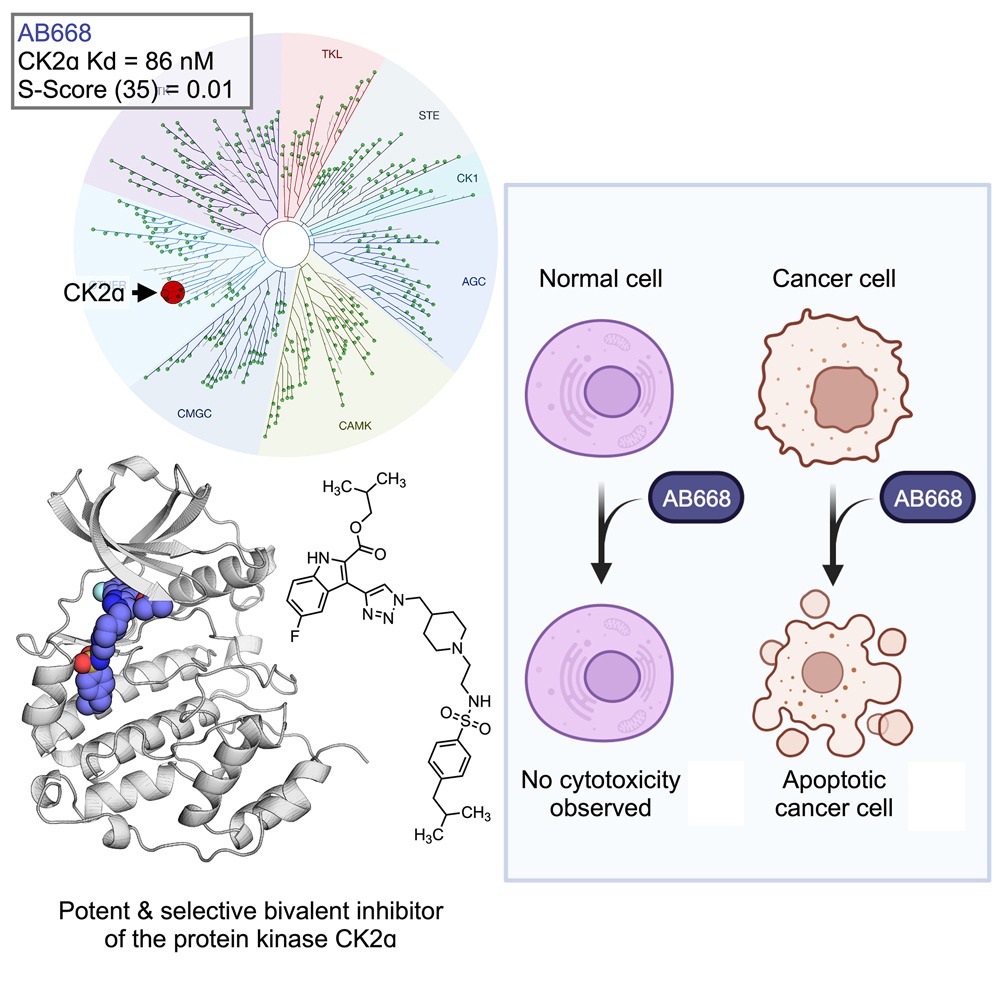
Figure: An allosteric inhibitor of CK2 with anti-cancer properties.
A) AB668 is a bivalent molecule that inhibits CK2 activity by binding simultaneously with high affinity (Kd: 86 nM) to its catalytic site and to an adjacent hydrophobic pocket.
B) AB668 induces of tumour cells death by apoptosis while preserving healthy cells.
Patent : US20230278983A1